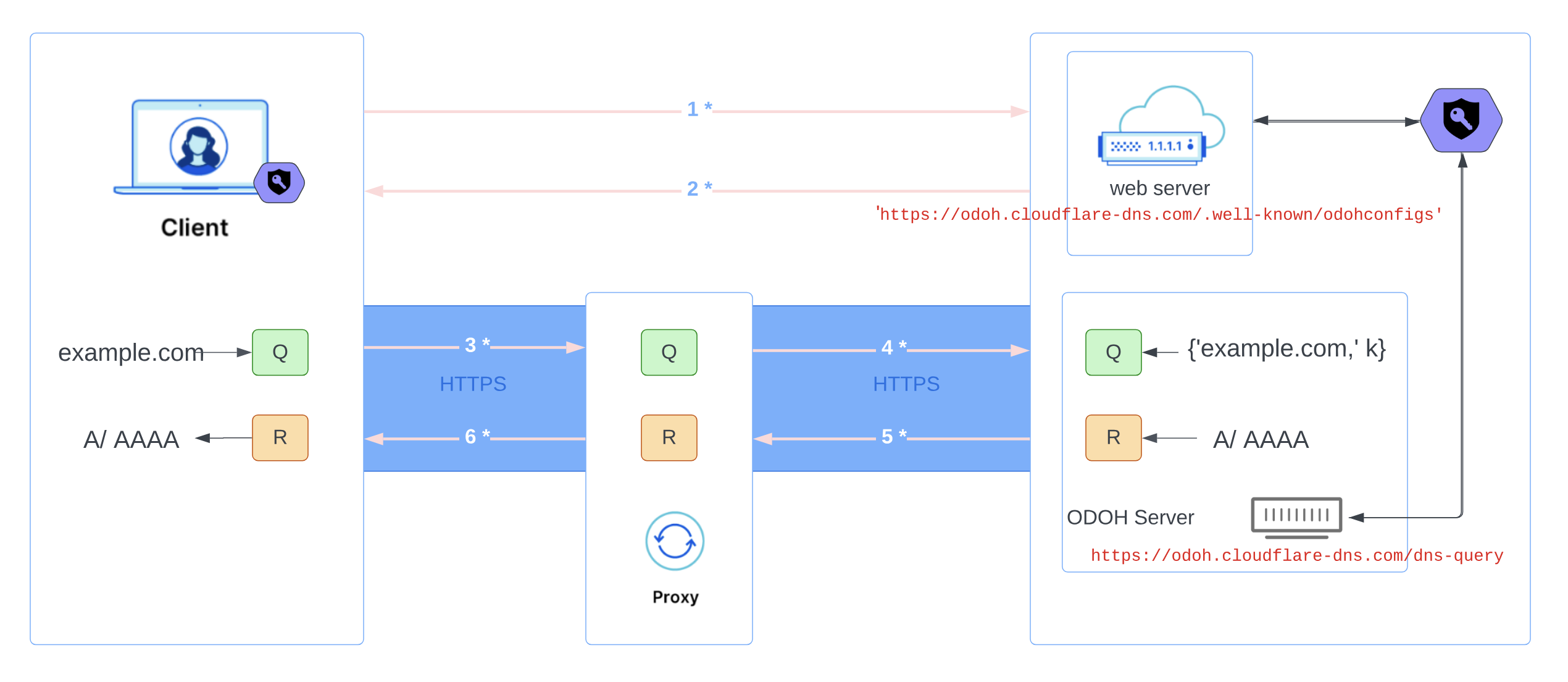
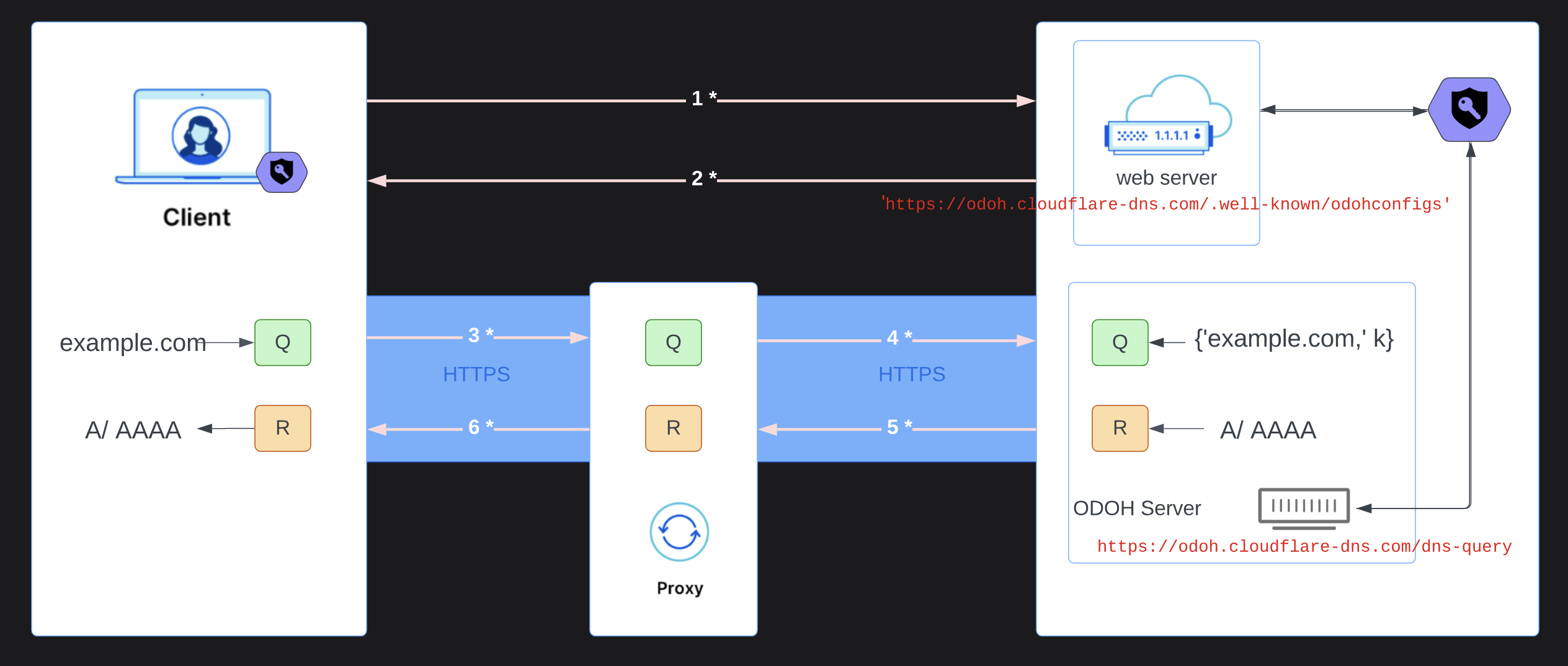
ODoH in the wild
ODoH - Oblivious DNS Over HTTPS - RFC 9230.
// proxy flag, switch case in go code.
1. DNS Goals
- Security - Can be achieved with a layer of ENCRYPTION.
- Integrity - Can be achieved with CHECKSUM.
- Privacy - Can be achieved with a PROXY between Client and the DNS Server.
| Feature | DNS | DOH | ODOH |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNS Request / Response is Encrypted | NO | NO | YES |
| DNS Server track the Client’s DNS requests | NO | NO | YES |
| DNS Transport is Encrypted | NO | YES | YES |
Note: DOH/ DOT/ DOQ all have same characteristic, except the transport layer is different.
//todo add example of 3 items
2. Publication
- ARXIV ODoH: A Practical Privacy Enhancement to DNS
- Oblivious DNS over HTTPS: ODoH RFC 9230
3. ODOH PARAMS
- odohConfig hosted URL.
- URL
https://odoh.cloudflare-dns.com/.well-known/odohconfigs
- URL
- domain to look up.
- Domain
example.com
- Domain
- which type of Resource Record, for the domain.
- RR Type
type AAAA-DNS_TYPE #28
- RR Type
- ODoH Server endpoint.
- endpoint
https://odoh.cloudflare-dns.com/dns-query
- endpoint
4. ODoH Exchange
| Activity | Function |
|---|---|
1. CLIENT REQ odohConfigs | REQUEST odohConfigs from DNS Server. |
2. SERVER SEND odohConfigs | PACK and SEND HPKE-SUITE and PUB-KEY as odohConfigs. |
3. CLIENT SEND ODoH Query | ENCRYPT and SEND DNS Query to ODOH-PROXY. |
4. PROXY FWD ODoH Query | FORWARD Encrypted DNS Query to ODNS Server. |
5. SERVER SEND ODoH Response | SEND Encrypted DNS Answer to ODOH-PROXY. |
6. PROXY FORWARD ODoH Query | FORWARD Encrypted DNS Answer to CLIENT. |
//todo add example of request and response output.
5. odohConfigs
- odohConfigs is a bundled info about the HPKE Suite and HPKE PUB-KEY, the ODoH Server is capable of communicating with.
- odohConfigs is a list of odohConfig. The Structure of odoh configs is defined as:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
struct {
uint16 kem_id;
uint16 kdf_id;
uint16 aead_id;
opaque public_key<1..2^16-1>;
} ObliviousDoHConfigContents;
struct {
uint16 version;
uint16 length;
select (ObliviousDoHConfig.version) {
case 0x0001: ObliviousDoHConfigContents contents;
}
} ObliviousDoHConfig;
where,
kem_idkdf_idaead_idspecify the Algorithm Identifier for KEM, KDF, and AEAD from HPKE Suite supported by the TARGET.public_keyis a byte stream of HPKE PUBLIC-Key derived from the Server’s HPKE Suite.versiondefines the odoh version used for packaging the odohConfigs. Current version is0x0001.lengthdefines the lenght of the odohConfigs as whole.
6. HTTPS Scheme Message Format
- All Messages use HTTP2 and above.
- ODoH Clients MUST NOT include any private state in requests to Proxies, such as HTTP cookies.
- ODoH PROXY MUST NOT send any Client-identifying information about Client to ODoH Server such as, “Forwarded” HTTP headers [RFC7239]/ HTTP cookies.
Example from RFC 9230, SECTION 4
A Client requests that a Proxy, dnsproxy.example, forward an encrypted message to dnstarget.example. The URI Template for the Proxy is https://dnsproxy.example/dns-query{?targethost,targetpath}. The URI for the Target is https://dnstarget.example/dns-query.
- CLIENT to PROXY
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
:method = POST
:scheme = https
:authority = dnsproxy.example
:path = /dns-query?targethost=dnstarget.example&targetpath=/dns-query
accept = application/oblivious-dns-message
content-type = application/oblivious-dns-message
content-length = 106
<Bytes containing an encrypted Oblivious-DoH Message/query>
- PROXY to TARGET.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
:method = POST
:scheme = https
:authority = dnstarget.example
:path = /dns-query
accept = application/oblivious-dns-message
content-type = application/oblivious-dns-message
content-length = 106
<Bytes containing an encrypted Oblivious-DoH Message/Query>
- SERVER to PROXY
1
2
3
4
:status = 200
content-type = application/oblivious-dns-message
content-length = 154
<Bytes containing an encrypted Oblivious-DoH Message/Response>
- PROXY to CLIENT
1
2
3
4
5
:status = 200
content-type = application/oblivious-dns-message
Proxy-Status: received-status=200
content-length = 154
<Bytes containing an encrypted Oblivious-DoH Message/Response>
7. Oblivious DoH Message Format
Oblivious DoH Message contains:
- A DNS message, which is either a Query or Response, depending on context.
- Padding of arbitrary length, which MUST contain all zeros.
Both DNS Query and Response messages use the ObliviousDoHMessagePlaintext format.They are encoded using the following structure:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
struct {
opaque dns_message<1..2^16-1>;
opaque padding<0..2^16-1>;
} ObliviousDoHMessagePlaintext;
struct {
uint8 message_type;
opaque key_id<0..2^16-1>;
opaque encrypted_message<1..2^16-1>;
} ObliviousDoHMessage;
message_type: A one-byte identifier for the type of message.- Query messages use message_type
0x01. - Response messages use message_type
0x02.
- Query messages use message_type
key_id: The identifier of the corresponding ObliviousDoHConfigContents key.encrypted_message: An encrypted message for the Oblivious Target (for Query messages) or Client (for Response messages).
8. ODoH Client Routines
8.1. encrypt_query_body (..) {..}
Constructs Oblivious DoH query from a DNS Query.
1
2
3
4
5
6
def encrypt_query_body(pkR, key_id, Q_plain)
enc, context = SetupBaseS(pkR, "odoh query")
aad = 0x01 || len(key_id) || key_id
ct = context.Seal(aad, Q_plain)
Q_encrypted = enc || ct
return Q_encrypted
Func takes public key of the resolver pkR, a key identifier key_id, and the plain query Q_plain as input parameters.
- Compute
encapsulation (enc)andcontextby BaseS-mode of HPKE Suite. - Construct additional authenticated-data
AAD. - Compute
CipherText (ct)of the query with the context and aad. - Form encrypted query
Q_encryptedas concat of enc and ct.
8.2. decrypt_response_body(..) {..}
Decrypts an Oblivious DoH response.
1
2
3
4
5
def decrypt_response_body(context, Q_plain, R_encrypted, resp_nonce):
aead_key, aead_nonce = derive_secrets(context, Q_plain, resp_nonce)
aad = 0x02 || len(resp_nonce) || resp_nonce
R_plain, error = Open(key, nonce, aad, R_encrypted)
return R_plain, error
Func takes context Encryption Context, Q_plain PlainText Query, R_encrypted Encrypted Response and resp_nonce response nonce as input params.
- Derive secrets:
aead_keyandaead_noncefrom the context and the response nonce. - Construct
additional authenticated data (AAD). - Decrypt encrypted response to obtain the
R_plain: plain response.
9. ODoH Server Routines
9.1. setup_query_context(..) {..}
1
2
3
4
def setup_query_context(skR, key_id, Q_encrypted):
enc_32 || ct_: = Q_encrypted
context = SetupBaseR(enc, skR, "odoh query")
return context
Func takes skR Resolver’s secret key, key_id Key identifier and Q_encrypted Encrypted ODoH query body as input params..
- Extract the encryption parameters:
enc_32andct_from Q_encrypted. - Set up the decryption context
contextusing BaseR-mode of HPKE Suite.
9.2. decrypt_query_body (..) {..}
1
2
3
4
5
def decrypt_query_body(context, key_id, Q_encrypted):
aad = 0x01 || len(key_id) || key_id()
enc_32 || ct_: = Q_encrypted
Q_plain, error = context.Open(aad, ct)
return Q_plain, error
Func takes context Decryption context, key_id Key identifier and Q_encrypted Encrypted ODoH query body as input params..
- Construct the
additional authenticated data (AAD). - Extract the encryption parameters:
enc_32andct_from Q_encrypted. - Compute PlainText
Q_plainthe encrypted query using aad and ct_.
9.3. derive_secrets (..) {..}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
def derive_secrets(context, Q_plain, resp_nonce):
secret = context.Export("odoh response", Nk)
salt = Q_plain || len(resp_nonce) || resp_nonce
prk = Extract(salt, secret)
key = Expand(odoh_prk, "odoh key", Nk)
nonce = Expand(odoh_prk, "odoh nonce", Nn)
return key, nonce
Func takes context Decryption context, Q_plain Plain query body and resp_nonce Response nonce as input params.
- Export the
secretfrom the context. - Compute
salt. - Derive
pseudo-random key (PRK), by HPKE method of Extract. - Derive
keyandnonce, by HPKE method of Expand.
9.4. encrypt_response_body (..) {..}
1
2
3
4
def encrypt_response_body(R_plain, aead_key, aead_nonce, resp_nonce):
aad = 0x02 || len(resp_nonce) || resp_nonce
R_encrypted = Seal(aead_key, aead_nonce, aad, R_plain)
return R_encrypted
Func takes R_plain Plain response body, aead_key Encryption key, aead_nonce Encryption nonce and resp_nonce Response nonce` as input params.
- Construct the
additional authenticated data (AAD). - Encrypt the response body
R_encrypted.